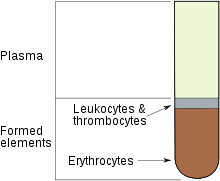
Homeostasis is defined as the maintenance of a fairly constant internal environment in an organism. All living organisms must be able to maintain a steady environment. Body fluid such as blood, lymph and tissue fluids make up the internal environment of the organism.